
Project Spotlight: dTRINITY
The Search for Sustainable Yield
The decentralized finance (DeFi) lending sector, a cornerstone of the on-chain economy, has long navigated fundamental economic tradeoffs. To attract liquidity, protocols must offer competitive yields to lenders; yet, to stimulate borrowing and protocol usage, they must provide low interest rates to borrowers. Historically, bridging this gap has most often relied on inflationary token rewards, creating a cycle of mercenary capital and questions around long-term sustainability. The search for a more capital-efficient and structurally balanced model remains a key challenge for the industry.
A new approach is emerging that rethinks the incentive structures of money markets. One of the projects at the forefront of this innovation is dTRINITY, the world’s first subsidized stablecoin protocol. Rather than directing all protocol-generated yield to the supply side or a treasury, dTRINITY redirects earnings from its reserve assets to directly subsidize borrowing costs. The core mission is to create a more robust equilibrium, where lower borrowing rates organically drive demand, leading to higher, more sustainable utilization and, in turn, healthier real yields for lenders.
Currently operational on the Fraxtal and Sonic networks, with expansions to Ethereum, Ronin, and Katana coming soon, dTRINITY introduces a novel primitive designed to enhance on-chain credit markets. This spotlight offers a detailed analysis of the protocol, from its novel architecture and risk management framework, to its core components: the dUSD stablecoin, Curve liquidity pools, and dLEND money markets—ultimately assessing how dTRINITY’s unique design positions it for a role of growing importance in the evolution of on-chain credit.
Subsidized Lending Flywheel
The protocol's innovation lies in how it allocates the yield generated from its stablecoin reserves. Instead of distributing this yield to passive holders, stakers, or a treasury, dTRINITY redirects it to the demand side of its own money market, dLEND. This creates a system of subsidized credit where the protocol effectively pays down a portion of the interest for users borrowing its native stablecoin, dUSD. Thus, dTRINITY’s mechanism is engineered to support a self-reinforcing flywheel that drives the protocol toward a higher, yet sustainable equilibrium between supply and demand.
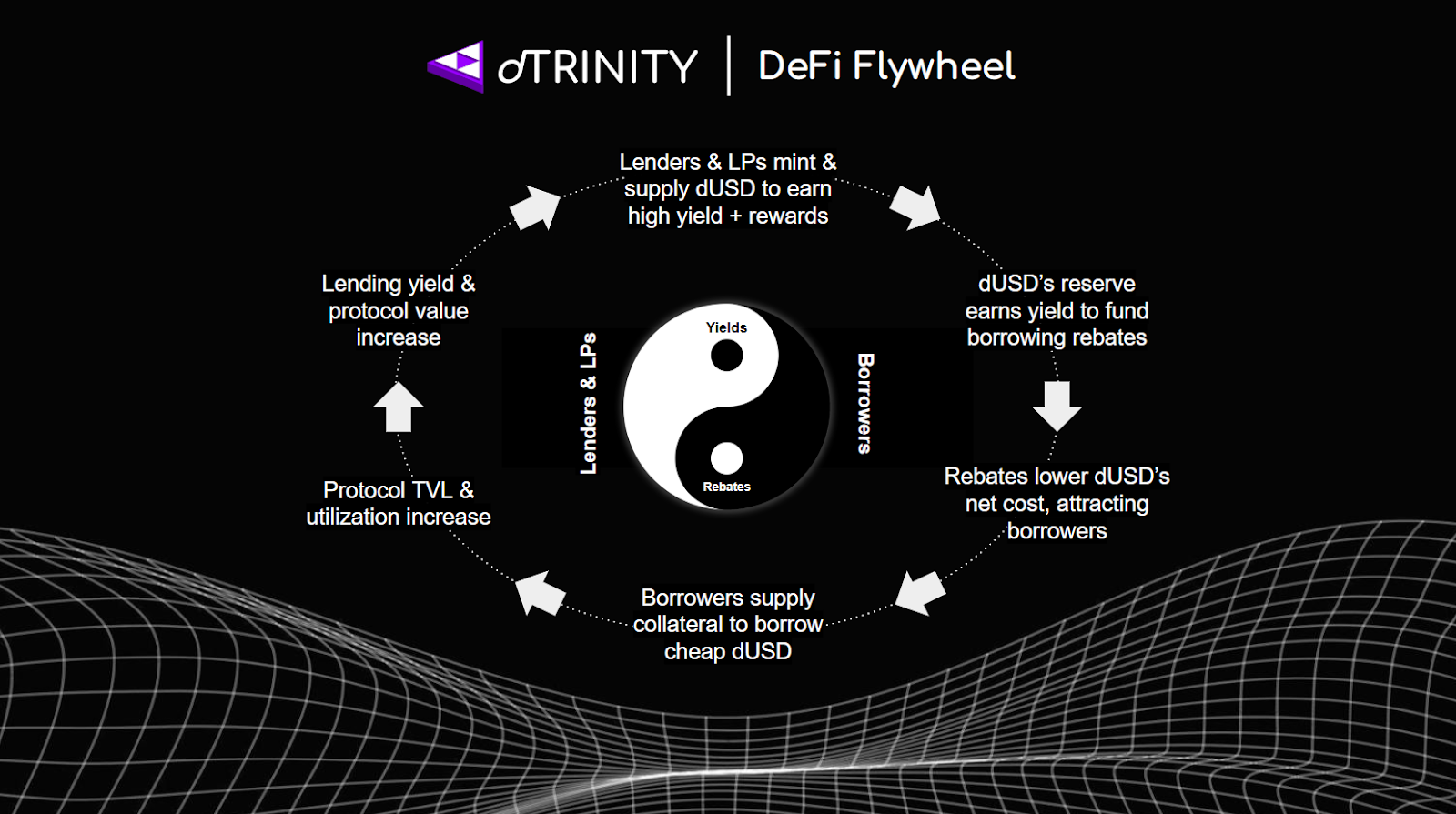
1. Subsidized Borrowing Stimulates Demand
The primary catalyst for the flywheel is the subsidized interest rate offered to dUSD borrowers. By redirecting reserve yield to offset borrowing costs, dLEND can offer a lower effective annual percentage rate (APR) than competing money markets. This makes stablecoin credit on dTRINITY more capital-efficient for activities such as leveraged yield farming or simply acquiring stablecoin liquidity, which directly stimulates borrowing demand.
2. Higher Credit Utilization
The increase in borrowing demand leads to a higher utilization rate for dUSD supplied by lenders within dLEND. In any lending protocol, the Supply APY is a direct function of the utilization rate, i.e., the proportion of supplied capital that is being actively borrowed. By structurally promoting borrowing, dTRINITY aims to maintain consistently high utilization.
3. Sustainable Yields for Lenders
High utilization directly translates into more attractive and sustainable yields for lenders. This model grounds lender yields in organic borrowing activity rather than inflationary token emissions, creating a more reliable and predictable return profile for lenders.
4. Attracting Deeper Liquidity
The prospect of earning stable, demand-driven yield incentivizes more lenders to mint and supply dUSD to the protocol. dUSD liquidity providers (LPs) on external exchanges like Curve also benefit from more fees thanks to subsidy-driven credit velocity and trading volume. This influx of capital from both lenders and LPs deepens the available liquidity, enabling the protocol to support greater subsidies and borrowing volume while reinforcing the entire flywheel.
By linking these four stages, dTRINITY aims to create a system where stimulating one part of the protocol directly benefits the other, fostering a capital-efficient ecosystem with more balanced supply and demand dynamics over the long term.
The dTRINITY Ecosystem
dTRINITY’s flywheel is powered by a ”trinity” of interconnected components, each designed to serve a specific function within the protocol. The three core components of dTRINITY are: a protocol-native stablecoin, external liquidity pools, and subsidized money markets. While dTRINITY’s economic model introduces a new primitive, its technical foundation is built upon secure, well-established DeFi infrastructure, combining innovation with robust design choices.
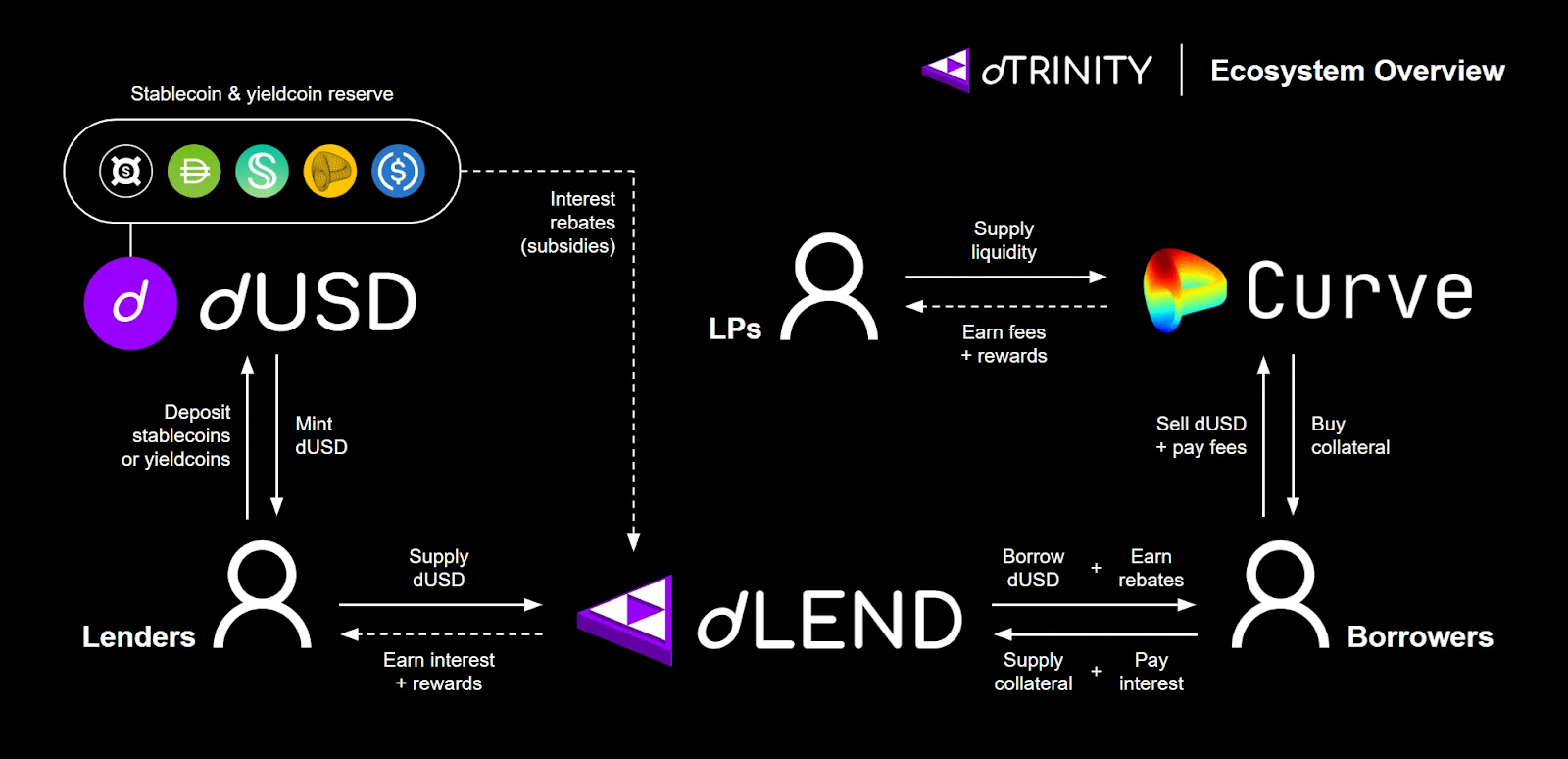
dUSD: The Reserve-Backed Stablecoin
The unified liquidity and credit layer within the ecosystem is dUSD, a decentralized ERC20 stablecoin designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US Dollar. Unlike purely algorithmic or crypto-overcollateralized stablecoins, dUSD is fully backed by an on-chain reserve composed primarily of price-stable and yield-bearing assets. The reserve includes established stablecoins like frxUSD and DAI, as well as their yield-generating counterparts (sfrxUSD and sDAI). It is the yield generated by these reserve assets that provides funding for the protocol's borrower subsidies.
To maintain its peg, dTRINITY relies on open minting and redemption of dUSD by arbitrageurs to naturally stabilize prices—similar to most stablecoins. dTRINITY also employs Stability Market Operations (SMO) and Algorithmic Market Operations (AMO) to optimize dUSD’s liquidity and price stability on decentralized exchanges (DEX). When dUSD trades below $1, the protocol can use its reserves to buy back dUSD from the open market via SMOs, reducing circulating supply and restoring the peg. Conversely, when dUSD trades above $1, the protocol can mint new dUSD and sell it to obtain fresh reserves via AMOs, increasing circulating supply while pushing down prices toward the peg. These protocol-managed mechanisms work in concert with market arbitrageurs to ensure the price stability and deep liquidity of dUSD.
To provide liquid yield opportunities for dUSD users, the protocol offers Staked dUSD (sdUSD)—a composable ERC4626 vault that automatically supplies dUSD deposits into dLEND to generate yield. The yield accrued by sdUSD is sourced from the borrowing interest paid by users on dLEND. This creates a direct incentive for users to supply dUSD to the protocol, which in turn deepens the liquidity available for borrowers and strengthens the flywheel. Additionally, the sdUSD vault receipt token effectively behaves like a yield-bearing stablecoin (YBS), which can then be integrated with other DeFi protocols to unlock secondary market liquidity or potentially more yields and utilities.
Curve Liquidity Pools
Secondary market depth is critical for peg stability and user confidence. External DEX liquidity pools, such as those on Curve, provide efficient swaps for both dUSD and sdUSD, as well as an operational venue to conduct SMOs and AMOs. They also facilitate LP yield opportunities:
- dUSD LPs can pair in pools like dUSD/frxUSD or dUSD/sfrxUSD, earning swap fees, rewards, and protocol incentives.
- sdUSD LPs can stack even more yield, since sdUSD already accrues lending yield from dLEND. In pools like sdUSD/sfrxUSD, LPs earn not only swap fees, rewards, and protocol incentives, but also the underlying yields of both sdUSD and sfrxUSD.
These layered opportunities expand yield options, attract deeper liquidity, and further reinforce the dTRINITY flywheel.
dLEND: The Subsidized Money Market
The credit engine of dTRINITY is dLEND, a decentralized, non-custodial money market that facilitates lending and borrowing for dUSD. Built as a fork of the widely audited and battle-tested Aave v3 codebase, dLEND provides the underlying infrastructure for the protocol's subsidized lending model.
The user journey on dLEND involves two primary actions:
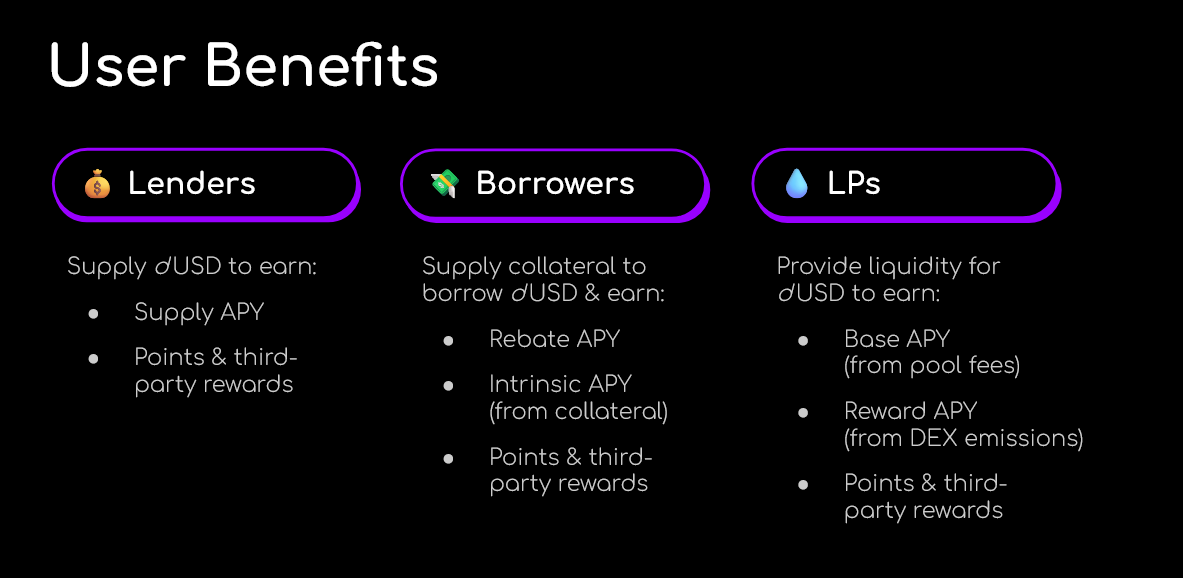
- Supplying Assets: Users can supply dUSD to earn yield or various forms of collateral, such as ETH, liquid staking tokens (LST), or other stablecoins and YBS, to borrow dUSD.
- Borrowing dUSD: After supplying collateral, users can borrow dUSD against their position. dUSD is the only asset that can be borrowed on dLEND, which focuses all borrowing demand on the protocol's native stablecoin. Collateral rehypothecation is disabled as a result, mitigating potential risks from nested leverage and bad liquidations to the protocol. Additionally, dUSD cannot be borrowed against itself, preventing subsidy arbitrage by loopers who repeatedly supply, borrow, and re-lend dUSD.
- Earning Rebates: Borrowers earn interest rebates (subsidies) as long as they maintain active debt in dUSD. The rebates are paid out continuously and can be claimed by borrowers on dLEND.
Incentives: The dTRINITY Points Program
To bootstrap liquidity and reward early participation, dTRINITY has implemented a native points program. Users can earn dTRINITY Points (dT Points) by performing actions that contribute to the protocol's growth, such as supplying assets to dLEND or providing liquidity on integrated DEXs . This program is designed to align the interests of the protocol with its early users, who are expected to be able to convert their dT Points into the future TRIN governance token, granting them a stake in the long-term success of the dTRINITY ecosystem.
Traction and Future Vision
A novel economic model requires a strong foundation of security and a clear vision for growth. dTRINITY has undergone a comprehensive security-first development process, including multiple smart contract audits from reputable blockchain security firms like Hats Finance, Halborn, Verichains, and Cyberscope.
dTRINITY first launched on Fraxtal L2 as its genesis network and has since expanded its operations to the Sonic network. This initial multi-chain presence allows it to tap into two distinct and growing ecosystems. As of September 2025, the protocol has attracted a combined Total Value Locked (TVL) of almost $7M across both chains. This early traction indicates that there is active interest from market participants in its subsidized borrowing model.
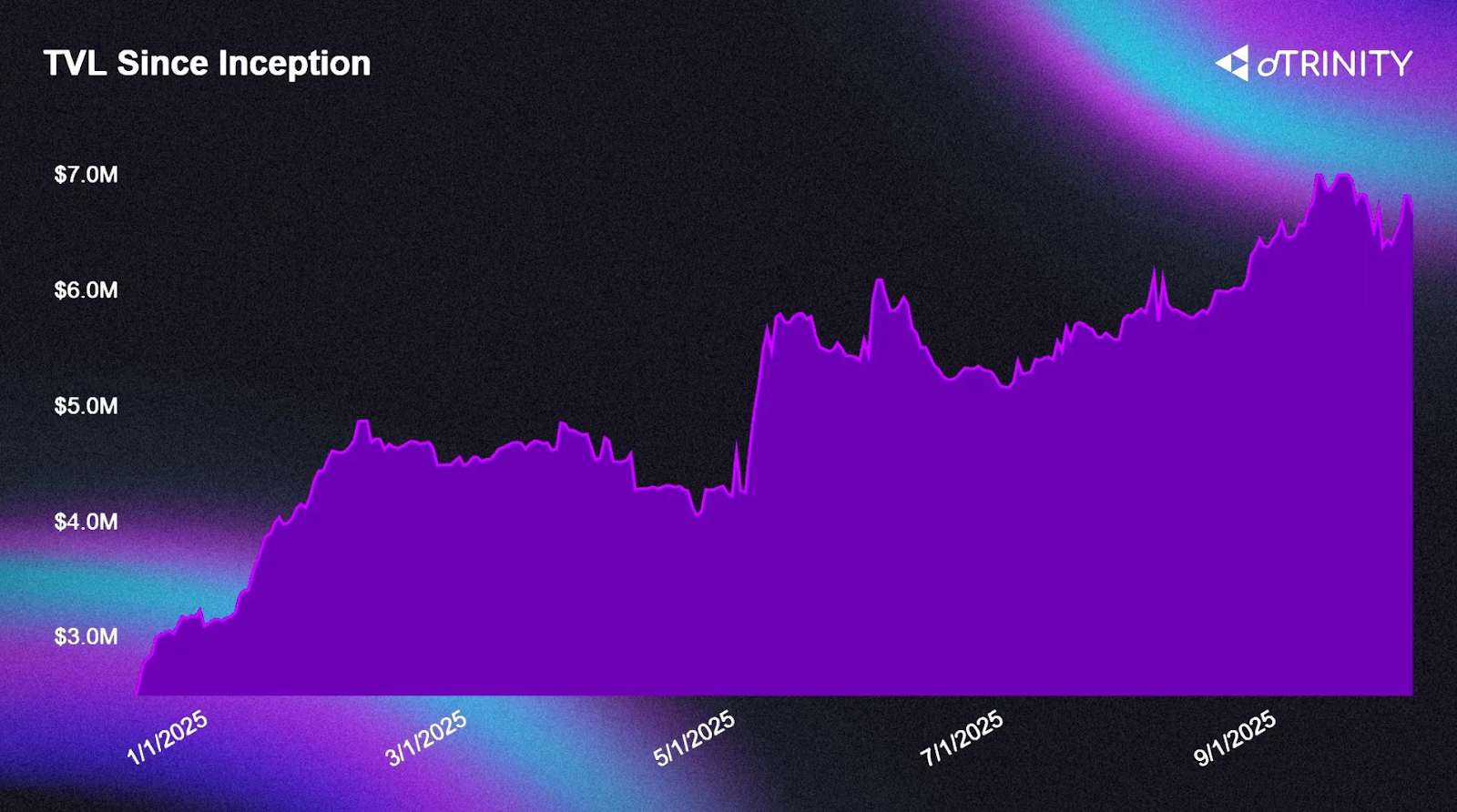
Combined TVL on all chains, including reserves, AMO liquidity, staking deposits, lending & collateral deposits
The dTRINITY team has outlined a clear roadmap for continued expansion. The next major milestone is the deployment onto the Ethereum mainnet, planned for Q4 of 2025. This move will bring the protocol to the largest DeFi ecosystem, significantly expanding its potential user base, liquidity, and TVL. Following the Ethereum launch, dTRINITY plans to expand to other emerging blockchains like Katana and Ronin, with the goal of establishing its subsidized lending primitive as a core tool for users across the broader DeFi landscape.
Conclusion
dTRINITY brings a novel twist on the standard DeFi money market. Its innovation is simple yet powerful: by redirecting yield from its reserve assets to subsidize borrowers, it directly addresses the high cost of capital that can limit growth. The long term goal is to align incentives for borrowers and lenders, organically supporting the protocol’s growth, removing the need for the ongoing inflationary rewards. The new layer is built smartly on top of a secure foundation, using a fork of the battle-tested Aave v3 codebase and plugging into core DeFi infrastructure like Curve.
This model represents a distinct evolution of the money market primitive. While foundational DeFi protocols primarily use borrower interest to reward lenders, dTRINITY introduces a new application for its system's yield. By redirecting reserve earnings to borrowers as a subsidy, the protocol makes the cost of capital its primary lever for stimulating growth, an innovation that shifts focus from solely relying on supply-side incentives.

About Piotr Kabaciński
Piotr is a Senior Researcher at Stablewatch focused on in-depth research and developing risk models for innovative stablecoin solutions. He holds a PhD in Ultrafast Spectroscopy from Politecnico di Milano, and has coauthored over 15 high-impact papers in leading scientific journals. He has worked in DeFi as an investor for venture capital firms Geometry and Synergis Capital, founded a startup, and worked as a Quantitative Researcher at Luban.